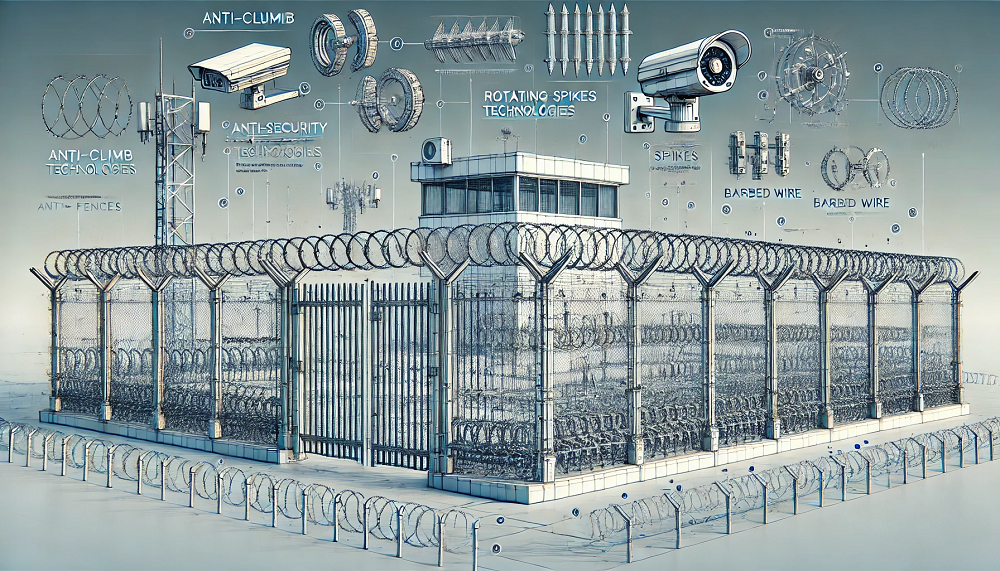
Recent advancements in anti-climb fence technology have revolutionized perimeter security, combining efficient physical barriers with intelligent monitoring systems. From perforated steel roofs to smart fencing with integrated sensors and AI-powered analytics, these innovations offer enhanced protection against unauthorized access while prioritizing safety and sustainability.
Cutting-Edge Climb Prevention
Recent advancements in anti-climb fence technology have introduced a range of innovative solutions to enhance perimeter security. These new technologies combine physical deterrents with smart monitoring systems to provide robust protection against unauthorized access. Some key innovations in anti-climb fencing include:
- Efficient physical barriers: Designs incorporating spikes, sloping fences, and anti-crawling nets make climbing extremely difficult for intruders.
- Intelligent monitoring systems: Real-time surveillance using cameras, infrared sensors, and radar technology to detect climbing attempts and trigger alarms.
- Integrated security solutions: Combining anti-climb fences with video analytics, artificial intelligence, and big data to improve threat detection and identification.
- Perforated steel anti-climb roofs: Seamlessly integrate with existing fences to create an impenetrable barrier, using durable perforated steel sheets mounted on tubular structures.
- Smart fencing with AI: Utilizes sensors, high-resolution cameras, and artificial intelligence to provide real-time monitoring, threat differentiation, and proactive security responses.
- Biometric access control: Incorporates fingerprint or facial recognition technology into fencing systems for enhanced authorized access management.
- Thermal imaging technology: Enables detection of heat signatures for effective surveillance in low-light or challenging weather conditions.
- Solar-powered fencing: Harnesses solar energy to power security features, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- High-strength materials: Advanced materials science has led to the development of reinforced steel and composite materials that enhance fence durability and resistance.
These innovations collectively improve the effectiveness of anti-climb high rise fencing by creating formidable physical and psychological barriers while leveraging cutting-edge technology for enhanced monitoring and rapid response capabilities.
Perforated Steel Anti-Climb Roofs
Perforated steel anti-climb roofs provide an effective and visually appealing solution for enhancing security in outdoor spaces. These roofs utilize perforated metal panels with strategically designed hole patterns that prevent climbing while allowing visibility and airflow. The perforations can be customized in various shapes and sizes to suit specific architectural styles and security needs.
Perforated steel roofs offer durability and corrosion resistance, making them suitable for long-term outdoor use in diverse environments. They can be integrated seamlessly with existing structures and landscaping, serving both functional and aesthetic purposes in areas such as industrial facilities, public spaces, and residential properties. The versatility of perforated steel roofs allows for creative design applications, including the incorporation of lighting elements to enhance visual appeal and security during nighttime hours.
Smart Fencing Systems with AI Integration
Smart fencing systems with AI integration represent a significant leap forward in perimeter security technology. These advanced systems combine traditional physical barriers with a network of sensors, cameras, and intelligent software to provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
AI algorithms analyze data from multiple sources, including vibration sensors, thermal cameras, and motion detectors, to differentiate between genuine security threats and benign events like wildlife activity or weather-related disturbances. This intelligent analysis significantly reduces false alarms while enabling rapid response to actual intrusions.
Smart fences can be customized for various applications, from securing critical infrastructure and international borders to protecting residential properties and construction sites. The integration of AI not only enhances detection accuracy but also allows for automated responses, such as activating alarms, deploying drones, or alerting security personnel, creating a proactive and efficient security ecosystem.
Solar-Powered Security Fencing
Solar-powered security fencing represents an innovative fusion of renewable energy technology and perimeter protection. These systems combine traditional fencing with integrated solar panels, serving the dual purpose of boundary demarcation and clean energy generation.
Solar fence panels are available in various configurations, from smaller integrated units to larger all-in-one fencing systems with solar-assist panels. Some advanced designs, like bifacial solar fences, can collect energy on both sides, offering up to 10% more electricity generation. These fences are versatile, finding applications in residential, industrial, agricultural, and even sensitive areas like military installations.
The core components typically include solar panels, a battery for energy storage, and an electric fence energizer, ensuring continuous operation even during low-light conditions. This eco-friendly approach not only reduces reliance on grid power but also offers low maintenance requirements, with most systems needing only occasional cleaning. Solar-powered electric fences are particularly advantageous for remote or temporary setups lacking direct access to electrical outlets, providing a sustainable and efficient solution for diverse security needs.
Weather-Resistant Coating Technologies
Weather-resistant coating technologies have advanced significantly, offering enhanced protection for various surfaces against harsh environmental conditions. These coatings are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and corrosive elements, making them crucial for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction.
Modern weather-resistant coatings often incorporate nanotechnology and advanced materials like ceramics, silicones, and epoxy resins to provide superior thermal stability and chemical resistance. For instance, ClimateCoating®-Nature, a high-tech coating for wooden components, utilizes reflective membrane technology and glass ceramic hollow spheres to keep surfaces cool even in dark colors while also protecting against swelling and shrinkage.
Additionally, thermal spray coatings like plasma spraying and High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) offer excellent wear and corrosion resistance for metal surfaces in aggressive environments. These innovative coating technologies not only extend the lifespan of materials but also contribute to energy savings and environmental protection, aligning with broader industry trends towards sustainability and efficiency.
Non-Conductive Mesh Barriers
GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) mesh fencing offers a versatile and durable solution for various industrial and commercial applications. This lightweight yet strong fencing material is characterized by its non-conductive, corrosion-resistant, and low-maintenance properties.
GRP mesh fencing is particularly suitable for environments where electrical insulation is crucial, such as railway tracks, airports, and industrial settings. Its radar and electromagnetic transparency make it ideal for use near sensitive equipment or in areas where signal interference must be minimized.
The fencing can be customized with different mesh sizes, colors, and specifications to meet specific requirements. Additionally, GRP mesh fencing’s resistance to UV radiation and extreme weather conditions ensures longevity and reliability in challenging environments, often lasting for decades with minimal upkeep.
Automated Threat Response Mechanisms
Automated threat response mechanisms have revolutionized cybersecurity by enabling rapid detection and mitigation of security incidents. These systems leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, identify potential threats, and initiate automated responses in real-time.
Key components include automated detection, which uses analytical techniques to continuously monitor networks for early threat identification; automated analysis, which examines detected threats and assesses their severity; and automated incident response, which takes immediate action to contain threats, such as isolating affected systems or blocking malicious traffic.
Advanced systems also incorporate security orchestration, integrating multiple security solutions for a coordinated defense, and incident playbooks that provide step-by-step guidance for specific security scenarios. By reducing the detection-response gap and minimizing human error, these mechanisms significantly enhance an organization’s ability to protect against evolving cyber threats.
Integration with Surveillance Systems
Integrated surveillance systems combine access control, video surveillance, and other security technologies into a unified platform, enhancing overall security effectiveness and operational efficiency. By integrating these components, organizations can achieve real-time monitoring, streamlined management, and improved incident response capabilities.
For example, when an unauthorized access attempt occurs, the integrated system can automatically trigger nearby cameras to focus on the area, providing visual verification and enabling quick action by security personnel. This integration also allows for centralized control through a single interface, reducing the workload on security staff and improving response times.
Additionally, integrated systems offer benefits such as preventing tailgating, managing unauthorized access more effectively, and providing valuable data insights for optimizing security protocols and business operations. As security threats evolve, the ability to seamlessly integrate various security technologies becomes increasingly crucial for maintaining robust and adaptive security measures.
DNA Grease for Anti-Climb
DNA grease is an innovative anti-climb technology that combines physical deterrence with forensic identification capabilities. This specialized grease contains unique synthetic DNA markers that transfer to anyone who comes into contact with it, allowing authorities to link suspects to specific locations or intrusion attempts.
When applied to fences, walls, or other potential climbing surfaces, DNA grease creates a slippery barrier that makes scaling difficult while simultaneously tagging intruders with an invisible, long-lasting forensic identifier. The DNA markers in the grease can persist on skin and clothing for several weeks, providing law enforcement with valuable evidence to aid in investigations and prosecutions.
This technology offers a dual benefit of both preventing unauthorized access and enhancing the ability to identify and apprehend perpetrators, making it an effective addition to integrated security systems for high-risk facilities, critical infrastructure, and other sensitive locations.
Where Do We Go From Here?
As the field of perimeter security continues to evolve, innovative anti-climb technologies are at the forefront of protecting assets and ensuring safety. From perforated steel roofs to AI-integrated smart fencing and DNA grease, these advancements offer multi-layered protection against unauthorized access.
The integration of renewable energy sources, like solar-powered fencing, and the use of weather-resistant coatings further enhance the durability and sustainability of these systems. As threats become more sophisticated, the combination of physical barriers with intelligent monitoring and automated response mechanisms provides a robust defense against potential intruders.
By leveraging cutting-edge materials, artificial intelligence, and forensic technologies, modern anti-climb solutions not only deter and prevent unauthorized access but also aid in the identification and apprehension of perpetrators. As we look to the future, continued innovation in this field will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the landscape of perimeter security across various sectors, from critical infrastructure to residential properties.