Welcome to the dynamic and ever-evolving realm of the stock market and mutual funds. Here, fortunes are made and dreams realized as investors navigate the exciting world of financial markets. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just beginning your journey, this is the place to uncover the opportunities and intricacies of wealth creation. Join us as we explore the captivating landscape of stocks and delve into the fascinating dichotomy of growth and value stocks.
In the realm of the stock market, individuals can participate in Mutual funds the ownership of companies, both established giants and promising startups. By investing in stocks, individuals become stakeholders in these companies, sharing in their successes and failures. The stock market is a bustling marketplace where buyers and sellers come together, constantly evaluating and reevaluating the worth of these company shares. It’s a world that is influenced by a myriad of factors, including economic indicators, company performance, investor sentiment, and global events.
But the stock market isn’t the only way to invest. offer a diversified and professionally managed approach to investing. These funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and other securities. Mutual funds provide an opportunity for individuals to access a wide range of investment options, even if they have limited knowledge or time to manage their investments actively. It’s a popular choice for those seeking a hands-off approach or looking to leverage the expertise of professional fund managers.
Within the stock market, investors encounter two primary investment strategies: growth and value investing. Growth stocks represent companies that are expected to experience significant expansion and increased profitability in the future. These companies often reinvest their earnings into research and development, innovation, and market expansion. On the other hand, value stocks are those that are considered undervalued relative to their intrinsic worth. Investors in value stocks seek companies with solid fundamentals that may be temporarily overlooked or unappreciated by the market.
The growth versus value debate has long been a topic of discussion among investors. Both strategies have their merits, and the choice ultimately depends on an individual’s investment goals, risk appetite, and time horizon. Growth stocks can offer the potential for explosive returns but may come with higher volatility. Meanwhile, value stocks may provide stability and potential for long-term appreciation but could require patience as the market recognizes their value.
In the subsequent chapters, we will delve deeper into the fascinating dynamics of growth and value investing. We will explore their key characteristics, advantages, and considerations, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed investment decisions. So fasten your seatbelts, open your minds, and let us embark on this exhilarating journey into the heart of the stock market and mutual funds. Together, we will unlock the secrets to building a robust and rewarding investment portfolio.
What are Growth Stocks?
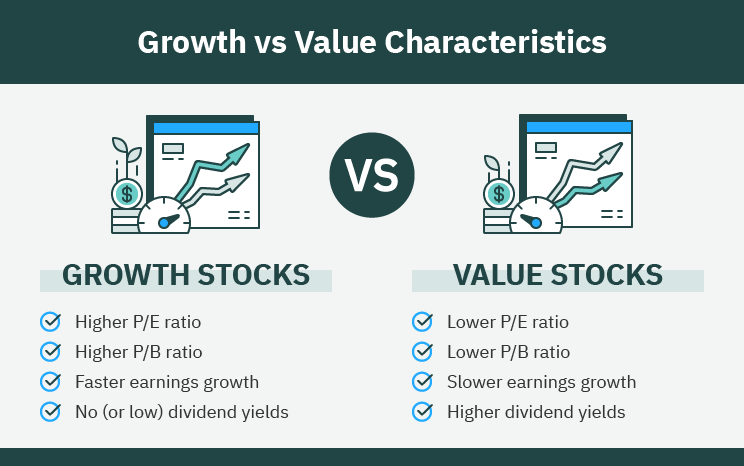
Growth stocks are shares of companies that exhibit substantial growth potential in the future. These companies typically have higher revenue and earnings growth compared to industry standards. They are often innovative and disruptive, operating in sectors like technology, healthcare, biotechnology, e-commerce, or renewable energy. Growth stock companies reinvest their profits back into the business to achieve targeted growth. They focus on expanding market share, investing in research and development, and capitalizing on emerging opportunities. While growth stocks may be more volatile and carry higher risks in the short term, they offer the potential for significant capital appreciation over the long term.
What are Value Stocks?
Value stocks, on the other hand, are shares of companies that are considered undervalued in the market compared to their intrinsic value. These companies are often well-established and have a history of good financial health. Value stocks can be found in mature or out-of-favor industries. They may be undervalued due to factors such as economic conditions, market sentiment, or the cyclical nature of the industry. Value stocks are known for their stability and reliability, and they typically offer regular dividend payouts. While they may not provide the same level of capital appreciation as growth stocks, they can be appealing to risk-averse investors seeking consistent returns and capital protection.
Key Differences between Growth Stocks and Value Stocks
- Meaning: Growth stocks represent companies with high growth potential, while value stocks are undervalued stocks in the market.
- Target Investors: Growth stocks are attractive to investors with high-risk appetite and a long-term investment horizon. Value stocks, on the other hand, appeal to risk-averse investors with lower-risk appetites, offering the possibility of capital protection and consistent returns.
- Returns: Growth stocks have the potential for higher returns in the long term, driven by capital appreciation. Value stocks may offer lower returns compared to growth stocks but focus on providing stable returns through dividends.
- Risk and Volatility: Growth stocks are generally more volatile and carry higher risks due to their aggressive growth strategies. Value stocks are considered less volatile and carry lower risks.
- Dividend Policy: Growth stock companies reinvest their profits for future growth and typically do not prioritize distributing dividends. Value stock companies are known for providing stable and consistent returns in the form of dividends.
- Valuation: Growth stock companies often have higher valuations compared to their current earnings or book value, reflecting their focus on future growth potential. Value stock companies tend to have lower valuations, indicating that they are undervalued in the market.
- Capital Appreciation: Growth stocks offer the potential for higher capital appreciation through increased stock prices over the long term. Value stocks may not provide significant capital appreciation but offer more stable returns throughout the investment period.
- Nature of Company: Growth stocks are often found in smaller, younger companies operating in high-growth sectors or those with disruptive business models. Value stocks are associated with well-established companies with stable earnings and financials in mature or out-of-favor industries.
- Valuation Ratios: Valuation ratios like the price-to-earnings (PE) ratio and price-to-book (PB) ratio tend to be higher for growth stocks compared to the industry average and their peers. Conversely, value stocks generally have lower valuation ratios compared to their industry average and peers.
Choosing between Growth Stocks and Value Stocks
The decision between growth stocks and value stocks ultimately depends on your investment goals, risk appetite, and investment horizon. If you have a long-term investment horizon, are willing to tolerate short-term volatility, and seek capital appreciation, growth stocks may be suitable for you. On the other hand, if you prioritize capital protection, prefer stable returns, and are risk-averse, value stocks may align better with your investment strategy.
Ideally, a well-balanced portfolio can include both growth stocks and value stocks to benefit from the advantages of each category while mitigating risks. It is crucial to thoroughly evaluate the fundamentals of a stock before investing and understand the correct entry and exit points in the market to maximize returns with minimal risks.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between Growth stocks and Value stocks is essential for constructing an investment portfolio that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By considering the characteristics, target investors, potential returns, risk profiles, and investment strategies associated with each type of stock, you can make informed decisions and optimize your investment outcomes.